-
 FAST SHIPPING
FAST SHIPPING
-
 COMPETITIVE PRICE
COMPETITIVE PRICE
-
 EXCELLENT AFTER-SERVICE
EXCELLENT AFTER-SERVICE
Solar energy grants in Catalonia: practical guide (2026)
Feb 16,2026Île-de-France Solar Incentives: Grants, VAT 5.5%, Steps
Feb 12,2026Solar Energy Grants in Andalusia 2026: A Practical Guide
Feb 06,2026What Size Solar Panel to Charge a 12V Battery (Wattage Guide)
Jan 30,2026Solar Panel to Accumulator Ratio: Size PV and Batteries Right
Jan 23,2026If you need to purchase related products, explore our outdoor power station catalog or contact us directly for more options.
To calculate how long a 200W power station will last, we need to break down the power usage, battery capacity, and the devices you're powering. The time a power station lasts depends on these main factors:
1. Battery Capacity:
Power stations typically specify their capacity in watt-hours (Wh). For example, a power station might have a 500Wh capacity, meaning it can provide 500 watts of power for 1 hour, or 1 watt for 500 hours.
Formula:
Duration (hours)=
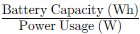
For instance, if you have a 200W power station and it's rated at 500Wh:
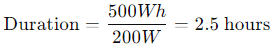
So, under perfect conditions, your power station could run for 2.5 hours if you were using a constant 200W.
2. Power Station Efficiency:
Most power stations aren’t 100% efficient, so you’ll lose a little energy through the conversion process (from DC to AC or through voltage conversion). Typically, power stations might have an efficiency rating around 85-90%. This means that if you have a 500Wh battery, you're only effectively able to use about 425-450Wh of it.
To account for this loss:
Effective Duration=
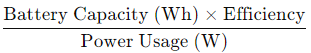
For a 90% efficient power station with a 500Wh capacity, the formula becomes
Effective Duration=
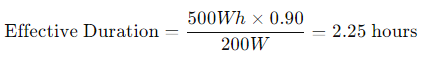
3. Power Station Load:
The devices you're running will have varying power consumption. Let’s take a deeper dive into the typical power usage of common devices to see how long the 200W power station would last under different loads:
Smartphone charger (15W):
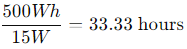
Your power station could charge a smartphone for over 33 hours.
Laptop (50W):
A power station could run a laptop for around 10 hours.
Mini Fridge (100W):
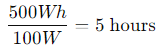
You could power a small fridge for about 5 hours.
Full-Sized Refrigerator (150W):

Your power station could run a larger refrigerator for just over 3 hours, assuming it runs constantly at 150W (which, in reality, would cycle on and off).
LED Light Bulb (10W):
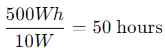
A low-wattage LED light bulb could run for a very long time.
4. Power Station Age & Battery Health:
As power stations age, the battery capacity naturally degrades, meaning your 500Wh power station will eventually only provide, say, 400Wh or even 350Wh after several years of usage. This will further reduce the runtime. Keep this in mind when planning long-term use.
5. Type of Battery Used:
Most modern power stations use lithium-ion or lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, both of which are efficient and last for hundreds or even thousands of charge cycles. However, different battery types have varying energy densities, which means some are more compact and others can store more power in a smaller form.
6. External Factors:
Other factors affect the duration:
Temperature: Extreme cold or heat can reduce battery efficiency.
Power Surges or Spikes: Devices like fridges or power tools often have power spikes that could deplete the battery faster than average.
Usage Pattern: A fridge, for example, won’t be running constantly. It may cycle on and off, reducing the overall average power consumption.
Example Scenario:
Let’s say you want to power a 50W device for as long as possible from a 200W power station with a 500Wh battery.
Device Power Consumption: 50W
Battery Capacity: 500Wh
Efficiency: 85%
So, we calculate:
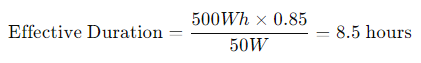
This means the power station could power a 50W device for roughly 8.5 hours in ideal conditions.
Conclusion:
The time your 200W power station lasts depends on how much power you're drawing and its battery capacity. If it has a 500Wh battery, and you're using around 200W, you could expect around 2-3 hours of run time, assuming no significant efficiency loss. However, smaller devices or lower power draw could extend this runtime significantly
←
Iraq's Power Market: "Crisis" and "Opportunity" – Systemic Collapse and the Potential of Distributed Energy
→
What are the differences between Deye BOS-G and Deye BOS-G Pro?
 +31610999937
+31610999937 [email protected]
[email protected] De Werf 11, 2544 EH The Hague, The Nederland.
De Werf 11, 2544 EH The Hague, The Nederland. WhatsApp: +1 (917) 257 2995/
WhatsApp: +1 (917) 257 2995/Copyright © 2023 Uni Z International B.V. VAT: NL864303440B01 All Rights Reserved
